This article is part of a series published by UReason about failure modes and effect analysis of essential components that are common in various industrial processes such as control valves, pneumatic actuators, electrical actuators, motors, and centrifugal pumps.
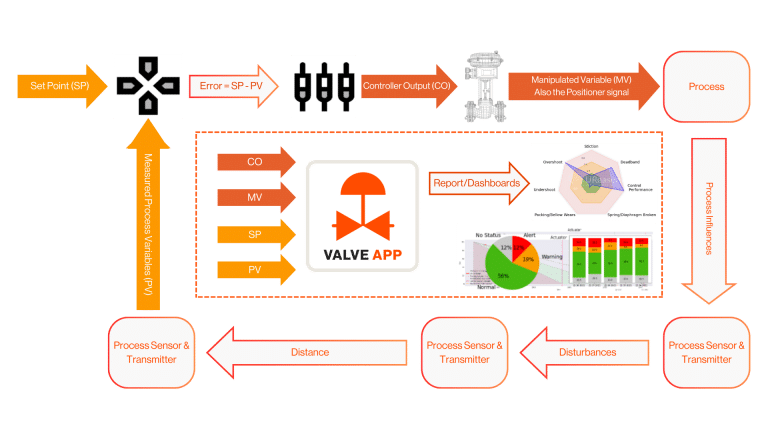
In the previous section we have seen what issues can occur to the controller of the control valve and what the consequences of these are. Our Control Valve App (CVA) provides several control performance insights by using the data you store in your process historians or logs.
Using the Controller Output (CO) and Manipulated Variable (MV – Positioner Signal) or combinations with the Setpoint (SP) and Controlled Variable (PV) the CVA provides valuable insights on:
1. Overshoot:
- Control overshoot refers to the extent to which the output of a control system exceeds the desired setpoint or reference value when it is trying to maintain a specific process variable. For example, if a control system is trying to maintain the temperature of a process at a certain level, an overshoot would occur if the temperature temporarily went above the setpoint before the control system can bring it back down to the desired level.
- Control overshoot can be caused by a number of factors, including poor tuning of the control system, high gain or sensitivity, external disturbances or noise, and mechanical wear and tear on the control valve or other components. It can also be caused by a lack of damping or damping that is too low, which can cause oscillations to build up and become more severe over time.
- Control overshoot can lead to instability and poor performance in a control system, as it can cause the output to fluctuate or oscillate excessively. To prevent or mitigate control overshoot, it is important to properly tune the control system, including selecting the appropriate control algorithm and gain settings, and to ensure that the control valve and other components are in good working condition. It may also be necessary to add damping or other stabilizing elements to the control system to reduce oscillations and improve its performance.
- Overshoot is calculated as a % of the valve setpoint and integrated over the observation period. A value under 2% is considered normal. A value between 2 and 5 % is considered an overshoot and will reported, by the CVA, as a warning. Overshoot more than 5% is high and will reported, by the CVA, as an alert.
2. Undershoot:
- Control undershoot refers to the extent to which the output of a control system falls below the desired setpoint or reference value when it is trying to maintain a specific process variable. For example, if a control system is trying to maintain the temperature of a process at a certain level, an undershoot would occur if the temperature temporarily goes below the setpoint before the control system can bring it back up to the desired level. Causes and consequences for undershoot are similar to overshoot (see above).
- Undershoot is calculated as a % of the valve setpoint and integrated over the observation period. A value under 2% is considered a normal process. A value between 2 and 5 % is considered undershoot and will be reported, by the CVA, as a warning. Undershoot more than 5% is high and will be reported, by the CVA, as an alert.
3. Hunting:
Hunting refers to oscillations or fluctuations in the output of a control system that are caused by the system’s own feedback. It occurs when a control system is trying to maintain a setpoint or reference value, but the output keeps overshooting or undershooting the setpoint, causing the control system to continually make adjustments. This can lead to an unstable and unpredictable control system that is difficult to maintain and optimize. Control loop hunting can be caused by several factors, including poor tuning of the control system, high gain or sensitivity, external disturbances or noise, and mechanical wear and tear on the control valve or other components. It can also be caused by a lack of damping or damping that is too low, which can cause oscillations to build up and become more severe over time.
Want to learn more about the Control Valve App? Try the demo or contact UReason!